
Scientists create these in a lab, using skin cells and other tissue-specific cells. They may one day play a role in solving a wide range of health problems. Scientists have used MSCs to create new body tissues, such as bone, cartilage, and fat cells. MSCs come from the connective tissue or stroma that surrounds the body’s organs and other tissues. At this stage, stem cells begin to differentiate.Įmbryonic stem cells can differentiate into more cell types than adult stem cells. In early pregnancy, the blastocyst stage continues for about 5 days before the embryo implants in the uterus, or womb.
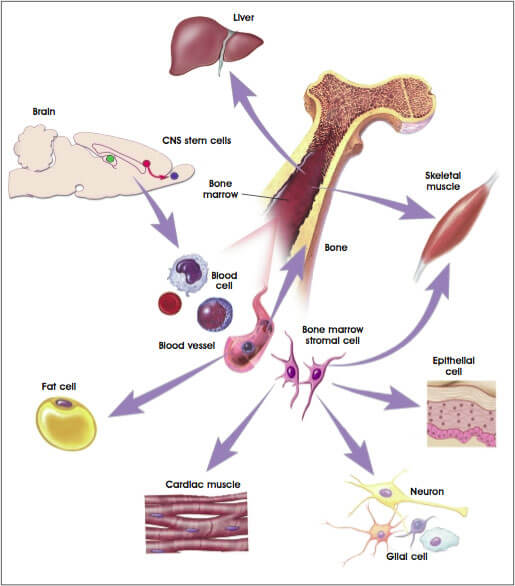
With the right stimulation, the cells can become blood cells, skin cells, and all the other cell types that a body needs. The term totipotent refer to the fact that they have total potential to develop into any cell in the body. The inner cell mass is where embryonic stem cells are found. an inner cell mass that will develop into the human body.an outer cell mass that becomes part of the placenta.Soon, and before the embryo implants in the uterus, this mass of around 150–200 cells is the blastocyst. This single-celled zygote then starts to divide, forming 2, 4, 8, 16 cells, and so on. When a sperm fertilizes an egg, these cells combine to form a single cell called a zygote. They will then implant a limited number of eggs to start a pregnancy. In IVF clinics, the doctors fertilize several eggs in a test tube, to ensure that at least one survives. When scientists take stem cells from embryos, these are usually extra embryos that result from in vitro fertilization (IVF). Embryonic stem cells come from a blastocyst that is 4–5 days old. The blastocyst contains stem cells and will later implant in the womb. Embryonic stem cellsįrom the very earliest stage of pregnancy, after the sperm fertilizes the egg, an embryo forms.Īround 3–5 days after a sperm fertilizes an egg, the embryo takes the form of a blastocyst or ball of cells. However, some evidence now suggests that they can differentiate to become other cell types, as well. In the past, scientists believed adult stem cells could only differentiate based on their tissue of origin. This division and regeneration are how a skin wound heals, or how an organ such as the liver, for example, can repair itself after damage. This means they can generate various cell types from the originating organ or even regenerate the original organ, entirely. They can stay non-dividing and non-specific for years until the body summons them to repair or grow new tissue.Īdult stem cells can divide or self-renew indefinitely. However, stem cells can be difficult to find. Scientists have found stem cells in tissues, including: Stem cells are present inside different types of tissue. In some parts of the body, such as the gut and bone marrow, stem cells regularly divide to produce new body tissues for maintenance and repair. They remain in this state until the body needs them for a specific purpose, say, as skin or muscle cells.ĭay-to-day living means the body is constantly renewing its tissues. The cells are in a non-specific state, but they are more specialized than embryonic stem cells. The body can use these stem cells whenever it needs them.Īlso called tissue-specific or somatic stem cells, adult stem cells exist throughout the body from the time an embryo develops. Share on Pinterest Stem cells can turn into any type of cell before they become differentiated.Ī person’s body contains stem cells throughout their life.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
